Column Aliases
- A column alias provides a way to create a clean or more descriptive header for a results set.
- A column alias cannot be used in a SELECT, WHERE, GROUP BY or HAVING clause due to the order of execution. You must refer to the original column name.
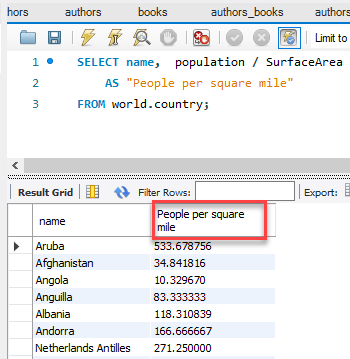
In the previous example, we created a new column that was a calculated value. The problem is that the column header is now population / SurfaceArea. However, we can rename the column header to something cleaner by creating a column alias. Look at the code snippet below.
Example:
SELECT name, population / SurfaceArea
AS “People per square mile”
FROM country;
We used the AS keyword then in quotes we put the new column alias of “People per square mile.” Which changes the column header as seen show below.
Results: