There has been an array of fake and false claims in the media about the severity and duration of the COVID-19 pandemic. This has led to very different responses by people throughout the country to government-based COVID-19 policies and recommendations (e.g., mask requirements, lockdown, social distancing, vaccinations).
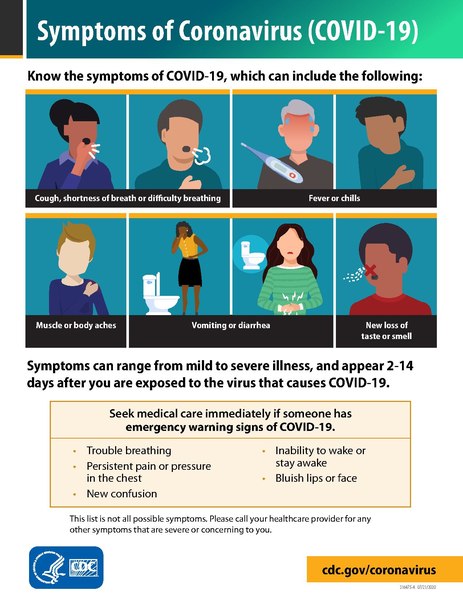 Symptoms of COVID-19 (English) by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention | Public Domain
Symptoms of COVID-19 (English) by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention | Public Domain
In one of the first studies to look at the impact of fake news on people's behaviors in 2021, researchers at the University College Dublin found that reading a fabricated news story (e.g., "certain foods will protect you against COVID-19" or "vaccines are not safe") just once could produce a small, but measurable change in how people intended to act toward the virus. Left unexamined by this study was the potential impact of repeated exposure to pandemic-related misinformation on people's thinking and acting.


 Watch on YouTube
Watch on YouTube
Have you been able to distinguish fake news about COVID-19 from the truthful and reliable information and guidance? How do you think other students and community members did with evaluating news about COVID-19? The following activities are designed to explore these questions.
Activity 1: Counter False News About COVID-19
It is the year 2021 and you have just been elected to serve as President Biden's marketing director. Biden has been struggling to increase the overall vaccination rates for the country and he has asked you to use your research and marketing skills to educate individuals who do not believe in or understand the risks of the COVID-19 virus.
- Identify individuals or groups who might not believe in the severity of the COVID-19 virus or think the virus is a hoax.
- Conduct Internet research and survey family and community members to identify possible explanations for why these individuals/groups developed inaccurate opinions about COVID-19 and what can be done about it.
- Then, explore the following resources to learn how to create persuasive scientific media:
- Develop a digital video or podcast to bring awareness and truthful information about COVID-19 to the individuals who might not believe in or understand the risks of the virus.
- Make sure to start by addressing any misconceptions they might have about COVID-19.
Activity 2: Evaluate Twitter Posts About COVID-19 in Regards to Civic, Political, and Private Life
- Explore posts about COVID-19 on Twitter (e.g., #covid19).
- Curate at least 15 tweets each from individuals engaging in: 1) Civic life; 2) Political life; and 3) Private life in a spreadsheet, Wakelet, slide deck, or virtual bulletin board (e.g., Padlet).
- Critically examine the differences in tweets between the three groups:
- What issues or policies are most frequently discussed?
- What types of visuals are used?
- What type of language is used?
- How do the individuals seek to influence others through their posts?
- Which types of posts got the most responses (shares, likes, retweets, comments)?
- How accurate, reliable, trustworthy, and credible are the posts?
- Create a screen recording or interactive image to present your findings.
- Interactive image:
- Start a new Google Drawings canvas.
- Upload a screenshot of selected tweets to the middle of the canvas.
- Insert text boxes and shapes to call attention to your findings.
- Add links to additional information (e.g., the original image source).
- Screenrecording:
Additional Resources
Connecting to the Standards
- Massachusetts Civics & Government Standards
- Distinguish among civic, political, and private life. (Massachusetts Curriculum Framework for History and Social Studies) [8.T4.3]
- ISTE Standards
- Digital Citizen
- 2c: Students demonstrate an understanding of and respect for the rights and obligations of using and sharing intellectual property.
- Knowledge Constructor
- 3a: Students plan and employ effective research strategies to locate information and other resources for their intellectual or creative pursuits.
- 3b: Students evaluate the accuracy, perspective, credibility and relevance of information, media, data or other resources.
- 3c: Students curate information from digital resources using a variety of tools and methods to create collections of artifacts that demonstrate meaningful connections or conclusions.
- 3d: Students build knowledge by actively exploring real-world issues and problems, developing ideas and theories and pursuing answers and solutions.
- Computational Thinker
- 5b: Students collect data or identify relevant data sets, use digital tools to analyze them, and represent data in various ways to facilitate problem-solving and decision-making.
- Creative Communicator
- 6a: Students choose the appropriate platforms and tools for meeting the desired objectives of their creation or communication.
- 6b: Students create original works or responsibly repurpose or remix digital resources into new creations.
- 6c: Students communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively by creating or using a variety of digital objects such as visualizations, models or simulations.
- 6d: Students publish or present content that customizes the message and medium for the intended audiences.
- DLCS Standards
- Ethics and Laws (CAS.b)
- Interpersonal and Societal Impact (CAS.c)
- Digital Tools (DTC.a)
- Collaboration and Communication (DTC.b)
- Research (DTC.c)
- English Language Arts > History/Social Studies Common Core Standards
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.6-8.6
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.6-8.7
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.6-8.8
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.5
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.6
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.7
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.9-10.8
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.6
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.7
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.8