The Five Clauses of the SELECT statement
- SELECT – the columns in the result set
- FROM – names the base table(s) from which results will be retrieved
- WHERE – specifies any conditions for the results set (filter)
- ORDER BY – sets how the result set will be ordered
- LIMIT – sets the number of rows to be returned
The clauses MUST appear in the order shown above.
Code Example:1 USE world;
2 SELECT name
3 FROM city
4 WHERE CountryCode = “AFG”
5 ORDER BY name
6 LIMIT 3
Results:
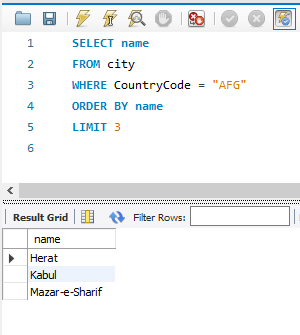
Let us break the statement line by line:
USE world;
- The USE clause sets the database that we will be querying. You typically have more than one database on your database server. You have to specify which database you are working in.
- The semicolon “;” indicates the end of a statement. You can execute multiple statements in sequence by defining each statement with a semicolon
SELECT name
- The SELECT clause defines the columns and column order that you want to retrieve in your results set. If you want to retrieve all of the columns from the base table you can simply use SELECT *
- You separate each column name with a comma “,” ex., SELECT name, CountryCode
- There is no trailing comma at the end of a column list
FROM city
- The FROM clause specifies the table that the results will be coming from
- You can specify multiple tables by using a JOIN clause, but we will address that topic at a future time
ORDER BY name
- The ORDER BY clause is not required but when used it defines the sort order of the results
- By default, the sort order is ascending. This is implicit However, you can use explicit syntax of ASC. If you want the sort, order to be descending you can use the keyword DESC.
- You can specify more than one column in an Order By statement separated by commas. The sort order DESC, ASC applies to each column individually. Below IS some examples
- ORDER BY population ASC, name DESC
- ORDER BY population, name (ASC is always implied if not explicitly stated)
LIMIT 5;
- If you only want to return a specified number of rows from the result set, you can use the LIMIT clause. This can be helpful when you want to test a query for accuracy that could potentially bring back a very large number of rows.
- The semicolon; defines the end of the statement.
Table 1. Column Specifications
| Source |
Option |
Syntax |
|
Base Table Value
|
Show all columns
|
|
|
Base Table Value
|
Column Name
|
Comma-separated list of column names
|
|
Calculated Value
|
Calculation result
|
Arithmetic expression
|
|
Calculated Value
|
Calculation result
|
Functions
|